Businesses should incorporate web design accessibility into their digital products not only because it’s the right ethical choice but also because it’s a sound business decision.
When we talk about "well-designed web products," we often mean such things as “users shouldn't strain their eyes to read the text or have trouble navigating.” But it's much broader than that. Good design also ensures that people with different abilities can fully participate and have a positive user experience with a product. A design that completely excludes people with disabilities from using the product cannot be per se considered “good.”
But before we delve into the nuances of how important accessibility in web design is and its benefits for businesses, let’s explore what the concept means.
Understanding web accessibility
So, what is web accessibility? To explore the concept, we’ll highlight the essential ingredients of web usability: user experience (UX) design and user interface (UI) design.

What is web accessibility?
Web accessibility means that web products are designed with no barriers that might prevent people with disabilities from interacting with them. These disabilities may be visual, auditory, tactile, communication-related, physical (e.g., missing limbs, cerebral palsy), cognitive, or neurological (e.g., epilepsy).
However, accessibility benefits not only people with disabilities. It also enables digital products to live up to the demands of modern users who expect web products to be convenient and require minimum effort. For example, accessibility can bring advantages to anyone in situations like:
- Using devices with small screens or challenging input modes
- Confronting situational limitations, such as a dim room or an environment that prohibits audio
- Dealing with temporary disabilities, such as a hand injury or lost glasses
- Working with a slow internet connection or limited bandwidth
Key web design accessibility principles
For digital design in general, and for web products specifically, designing for accessibility requires a well-thought-out UX and UI that subscribe to the following principles:
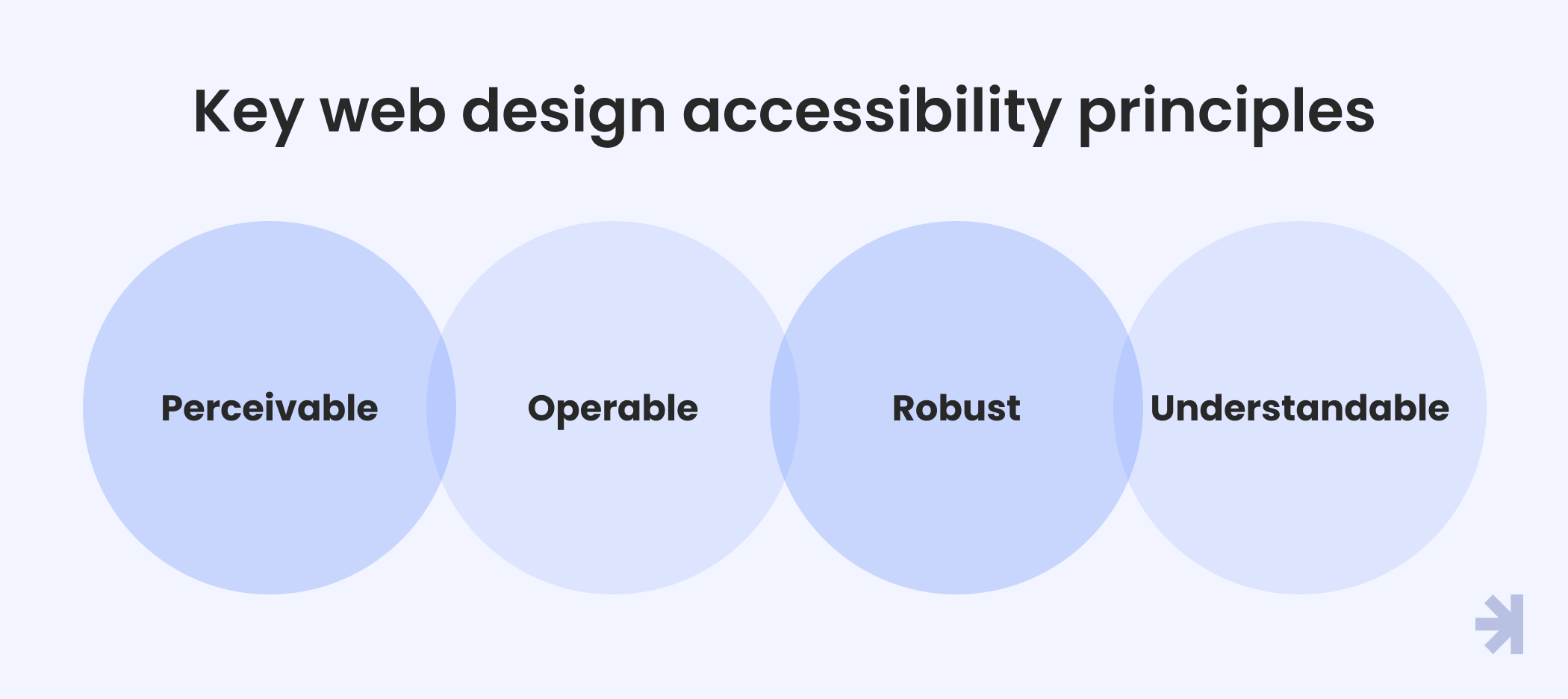
Perceivable
User interfaces should make it easy for people with various abilities to process information. Here are some interface elements to consider:
- Text size adjustment features
- Screen readers to convert text to audio
- Text transcripts for audio and video content
- Audio conversion of text and narration of video content
- Sign language interpretation of audio and video media
- Adjustable audio volume
- Discernible contrast between design elements, like foreground and background colors
- Adequate time for users to process content (for instance, content blocks should not scroll too fast, and session time limits should not be too short)
To quickly assess if a web product is perceivable, you can check whether its design allows people with visual or auditory limitations to process all content.
Operable
People with disabilities should be able to successfully navigate and use the web product’s control buttons, input fields, and other interface components. The following elements can help:
- Keyboard navigation to control all interface components
- Voice navigation to control functions without using touchpads, keypads, or keyboards
- Warnings about and an option to bypass flashing content that may cause photosensitive reactions, like seizures
- Straightforward and easy-to-navigate content layout
- Undo functionality to correct accidental activations
- Interface components, such as buttons and links, that are large enough to activate easily
To quickly assess the operability of a web product, ask yourself if people new to the platform could navigate and control its interactive elements without difficulty or confusion. For example, check whether people who are unable to maneuver a mouse or tap a button can still fully access the product’s functions.
Understandable
The ability to perceive and operate a digital product does not always translate to understanding it. Here are some design elements that can help users fully understand your web solution:
- Avoiding the use of or providing definitions for jargon and unusual words
- Concise and easy-to-grasp content
- Short captions for visuals, such as charts, images, and video files
- Labels for graphical components, such as buttons, icons, and forms
- Straightforward instructions for complex fields and functionalities
- Error messages to explain the causes of errors and suggest how to correct them
- Opportunities to review input before submitting a form or review options before activating certain functionalities
To determine if your interface is understandable, check whether a first-time user can easily understand what you’re trying to communicate with your content.
Robust
Users should have a seamless experience with your web product as they move across platforms, devices, and browsers. Here are the two key conditions to make that happen:
- Content is compatible with and responsive to different platforms, devices, and browsers
- The interface components are compatible with assistive technologies
You know your web product is robust when it works just as well with an outdated browser as it does with newer ones. It should also be just as easy to navigate on a mobile devices as it is on a desktop.
These are only some of the elements to consider if you want to achieve optimal conditions. It’s easy to see that designing an accessible digital product is complex and time-consuming. Unsurprisingly, these aren’t the only challenges. In the next section, we discuss two important challenges tangentially related to web accessibility design.
Challenges to designing accessible web pages and products
Businesses often acknowledge the need for website accessibility but have difficulties making it happen. Three of the top challenges they commonly encounter are:
Poor Education and Awareness
- Misconceptions persist regarding the concept of websites accessible, particularly in terms of compliance with WCAG standards.
- Lack of knowledge about the disabled population's size and spending power.
- Difficulty in conveying the importance of accessibility across organizations.
Lack of Capability and Governance
- Another formidable challenge is the dearth of clear ownership and responsibility when it comes to website accessibility.
- Organizational structural barriers often impede access improvements, with resource limitations and the need to balance accessibility against other priorities acting as significant roadblocks.
- Additionally, there is a concerning perception that accessibility is primarily an individual's task within an organization, rather than a collective effort.
Accessibility as an Afterthought
- Accessibility concerns are frequently relegated to later stages of web page development, which is a critical challenge in ensuring comprehensive digital inclusion.
- Overreliance on design and development teams to address accessibility issues leads to suboptimal results.
Although it comes with challenges, once you consider why accessibility is important, you’ll see that it’s all worth it.
The importance of accessibility web design: An ethical and profitable choice
So, why is web accessibility important?
People run to the web for answers when they’re grappling with issues related to education, employment, healthcare, and other important aspects of life. Many also go online to complete everyday tasks, including buying groceries, finding their way around a new neighborhood, and setting an appointment with the doctor. It’s only fair that everyone has easy access to web resources. And that’s what web accessibility aims to achieve.
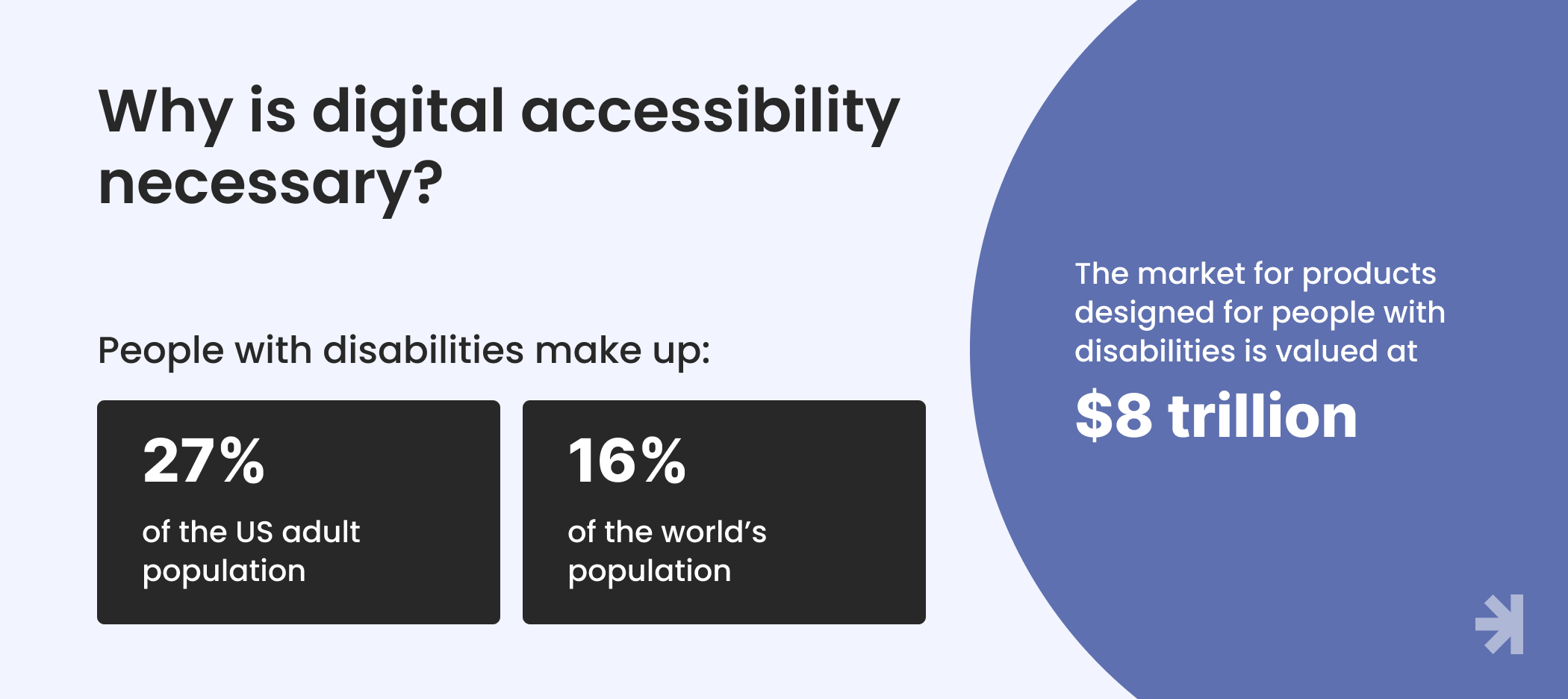
Web accessibility is not only an ethical imperative, but it’s also a smart business decision. After all, people with disabilities make up 27% of the US adult population and 16% of the world’s population. The market for products designed for people with disabilities is valued at a whopping $8 trillion. Those who fail to achieve accessible design lose out on a lucrative opportunity.
Next, we’ll delve deeper into the business benefits of web accessibility.
Why is digital accessibility necessary for your bottom line? Five top reasons
As the data presented above reveal, accessibility in web design brings more than just social benefits. It also impacts your bottom line. Despite these benefits, many IT professionals still fail to prioritize accessibility. One survey revealed that only 31% of organizations take accessibility into account when doing customer research. Meanwhile, it’s a vital ingredient of a web product’s success.
Why is digital accessibility necessary, and why does it have such a good ROI? Here are a few reasons.
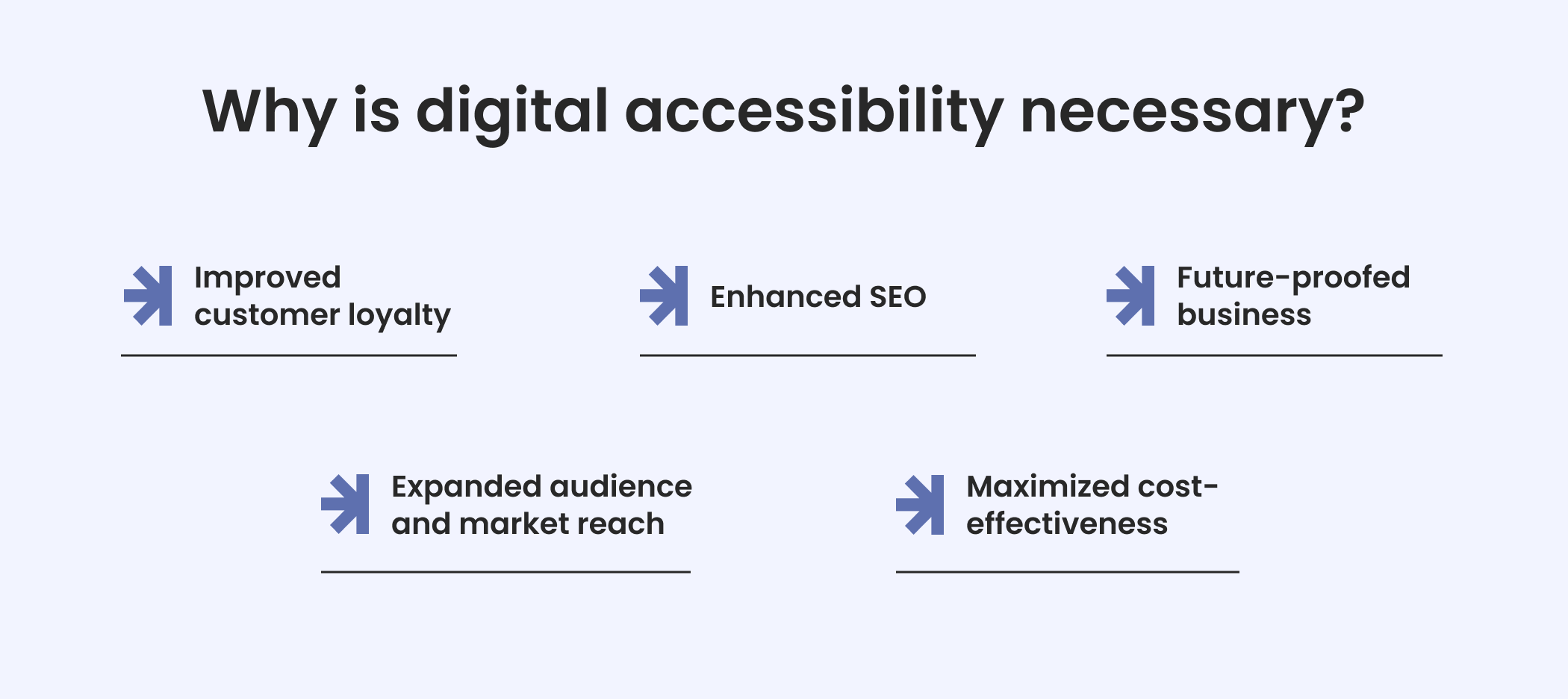
1.Expanded audience and market reach
As mentioned above, people with disabilities make up a significant market, and web accessibility allows you to reach them.
Then there’s the curb-cut effect: a phenomenon where features created to accommodate people with disabilities end up delighting a broader group of users. Many of the technologies we enjoy were originally designed for people with disabilities, including keyboards, screen readers, and audiobooks.
So, don’t be surprised if the color contrast combination you meticulously designed for people with visual impairments is also the reason most users choose your web app.
2.Improved customer loyalty
A web product that’s hard to navigate can damage your brand’s reputation. A good user experience, on the other hand, will have customers coming back for more. Accessibility enhances your brand’s image and attracts loyal customers.
Moreover, socially conscious consumers are drawn to brands that support their values. A survey commissioned by Facebook revealed that 59% of consumers stick with brands that advocate for diversity and inclusion. Your ethical practices are bound to feed your bottom line.
3.Enhanced SEO
Accessibility best practices, such as adding alternative text to images and writing highly readable content, translate to SEO brownie points. Although search engines like Google don’t explicitly consider accessibility in ranking websites, the more understandable your web product is the easier it is to rank. A user-friendly interface also reduces bounce rates and keeps users coming back for more (i.e., more traffic).
In summary, you create a web page that earns favor from search engines, including web browsers.
4.Future-proofed business
Considered the wealthiest cohorts, seniors and older professionals are already a lucrative market. As a matter of fact, the silver economy is expected to become even more sizeable until 2030, as it grows by 3.2 percent every year.
People over 60 years old will make up 22% of the global population by 2050. Improving web accessibility and making your web products friendly to this population, who will gradually need more accessible web products, essentially future-proofs your business.
5.Maximized cost-effectiveness
Investing in UX during the early stages of a project can cut the length of the development cycle down by half. Doing away with accessibility efforts may appear budget-friendly in the short term, but it can run up expenses in the long run. It could also cost your business because unhappy customers will opt out of your subpar product offering.
The benefits of accessibility in business outweigh the costs of investing in it, as the case studies in the next section demonstrate.
Why digital accessibility is necessary: Real-life success stories
A solution that delivers a prime user experience to all populations in your audience (including people with disabilities) increases customer satisfaction, promotes positive word of mouth, saves money, and boosts sales.
For instance, the case of American Airlines demonstrated the cost-effectiveness of incorporating usability into the design phase. This allowed them to reduce expenses to fix usability issues by 60-90%.
Another example is the Staples case. Their redesigned e-commerce platform saw an 80% boost in traffic and a 67% increase in repeat customers compared to before the redesign. Drop-off rates also fell by 45%.
So, design usability (with accessibility as its core component) is a standard that businesses, both big and small, should aspire to.

Conclusion
Web accessibility standards and accessibility solutions are essential for businesses aiming to enhance their online presence. Businesses must strive for web accessibility because it feeds the bottom line while providing social benefits.
By integrating accessibility requirements into the design process from the outset, businesses can avoid costly retrofits and ensure a smoother development journey.
Moreover accessible web design boosting SEO to expanding market reach and inspiring customer loyalty, accessibility brings benefits that make the investment worth it.
Reach out to MagicFlux for design accessibility that’s done right. With our specialized expertise, you can ensure that your design accessibility is done right, aligning with accessibility standards and benefiting both your business and society as a whole.
FAQ
1. How does web accessibility improve the user experience?
The importance of accessible websites is highlighted by the innovation it fosters. Design improvements meant to help individuals with special needs end up benefitting all users as they make online browsing, input control, and other user interactions more convenient.
2. How does web accessibility expand your market reach?
The importance of accessibility in web design lies in its ability to not only tap a sizeable market comprised of people with disabilities but also to reach a growing aging population who will need adaptations and increasingly demanding modern consumers.
3. How can businesses start implementing web accessibility?
Begin by following web accessibility guidelines like WCAG. Work with agencies like MagicFlux, specializing in ensuring your web content, including audio content, is keyboard accessible with features like tab key navigation and proper alt text, making your content accessible across various operating systems.
4. What’s the difference between web accessibility and accessibility in digital design?
Both web accessibility and accessibility in digital design concern UX and UI elements that contribute to a premier user experience for people with disabilities. But while accessibility in digital design covers all digital solutions (web, desktop, and mobile), web accessibility focuses exclusively on web solutions.
5. What are Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)?
Web content accessibility guidelines (WCAG) are a set of internationally recognized guidelines developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) to ensure web content is accessible to people with disabilities.
6. What is the importance of creating an accessible website?
Creating an accessible web design is vital as it ensures that all web users, including those with disabilities (low vision, visual impairment, cognitive disabilities and so on) , can effectively navigate web pages, use web form and use site search, promoting inclusivity and equal access to same information and services.

